DAY 9
JAVA COLLECTION FRAMEWORK
Collections in java is a framework that provides an architecture to store and manipulate the group of objects.
All the operations that you perform on a data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, deletion etc. can be performed by Java Collections.
Java Collection simply means a single unit of objects. Java Collection framework provides many interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque etc.) and classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet etc).
Collection represents a single unit of objects i.e. a group.
All the operations that you perform on a data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, deletion etc. can be performed by Java Collections.
Java Collection simply means a single unit of objects. Java Collection framework provides many interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque etc.) and classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet etc).
Collection represents a single unit of objects i.e. a group.
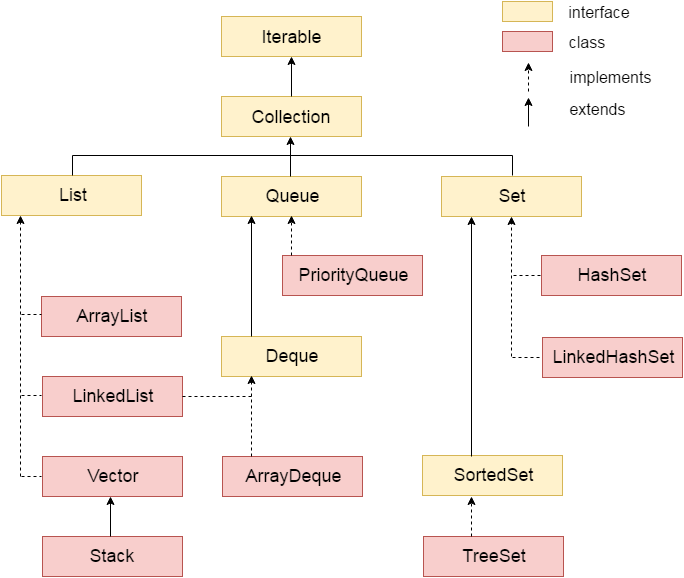
Hierarchy of Collection Framework:
Let us see the hierarchy of collection framework.The java.util package contains all the classes and interfaces for Collection framework.
Methods of Collection interface
There are many methods declared in the Collection interface. They are as follows:| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | public boolean add(Object element) | is used to insert an element in this collection. |
| 2 | public boolean addAll(Collection c) | is used to insert the specified collection elements in the invoking collection. |
| 3 | public boolean remove(Object element) | is used to delete an element from this collection. |
| 4 | public boolean removeAll(Collection c) | is used to delete all the elements of specified collection from the invoking collection. |
| 5 | public boolean retainAll(Collection c) | is used to delete all the elements of invoking collection except the specified collection. |
| 6 | public int size() | return the total number of elements in the collection. |
| 7 | public void clear() | removes the total no of element from the collection. |
| 8 | public boolean contains(Object element) | is used to search an element. |
| 9 | public boolean containsAll(Collection c) | is used to search the specified collection in this collection. |
| 10 | public Iterator iterator() | returns an iterator. |
| 11 | public Object[] toArray() | converts collection into array. |
| 12 | public boolean isEmpty() | checks if collection is empty. |
| 13 | public boolean equals(Object element) | matches two collection. |
| 14 | public int hashCode() | returns the hashcode number for collection. |
Iterator interface
| Iterator interface provides the facility of iterating the elements in forward direction only. |
Methods of Iterator interface
There are only three methods in the Iterator interface. They are:| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | public boolean hasNext() | It returns true if iterator has more elements. |
| 2 | public Object next() | It returns the element and moves the cursor pointer to the next element. |
| 3 | public void remove() | It removes the last elements returned by the iterator. It is rarely used. |
Java ArrayList class
 Java ArrayList class uses a dynamic array for storing the elements. It inherits AbstractList class and implements List interface.
Java ArrayList class uses a dynamic array for storing the elements. It inherits AbstractList class and implements List interface.The important points about Java ArrayList class are:
- Java ArrayList class can contain duplicate elements.
- Java ArrayList class maintains insertion order.
- Java ArrayList class is non synchronized.
- Java ArrayList allows random access because array works at the index basis.
- In Java ArrayList class, manipulation is slow because a lot of shifting needs to be occurred if any element is removed from the array list.
Hierarchy of ArrayList class
As shown in above diagram, Java ArrayList class extends AbstractList class which implements List interface. The List interface extends Collection and Iterable interfaces in hierarchical order.ArrayList class declaration
Let's see the declaration for java.util.ArrayList class.Constructors of Java ArrayList
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | It is used to build an empty array list. |
| ArrayList(Collection c) | It is used to build an array list that is initialized with the elements of the collection c. |
| ArrayList(int capacity) | It is used to build an array list that has the specified initial capacity. |
Methods of Java ArrayList
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void add(int index, Object element) | It is used to insert the specified element at the specified position index in a list. |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | It is used to append all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection's iterator. |
| void clear() | It is used to remove all of the elements from this list. |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in this list of the last occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain this element. |
| Object[] toArray() | It is used to return an array containing all of the elements in this list in the correct order. |
| Object[] toArray(Object[] a) | It is used to return an array containing all of the elements in this list in the correct order. |
| boolean add(Object o) | It is used to append the specified element to the end of a list. |
| boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) | It is used to insert all of the elements in the specified collection into this list, starting at the specified position. |
| Object clone() | It is used to return a shallow copy of an ArrayList. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in this list of the first occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the List does not contain this element. |
| void trimToSize() | It is used to trim the capacity of this ArrayList instance to be the list's current size. |
Java Non-generic Vs Generic Collection
Java collection framework was non-generic before JDK 1.5. Since 1.5, it is generic.Java new generic collection allows you to have only one type of object in collection. Now it is type safe so typecasting is not required at run time.
Let's see the old non-generic example of creating java collection.
For more information of java generics, click here Java Generics Tutorial.
Java ArrayList Example
OUTPUT:
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
Two ways to iterate the elements of collection in java
There are two ways to traverse collection elements:- By Iterator interface.
- By for-each loop.
Iterating Collection through for-each loop
OUTPUT:
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
Java LinkedList class
Java LinkedList class uses doubly linked list to store the elements. It provides a linked-list data structure. It inherits the AbstractList class and implements List and Deque interfaces.
The important points about Java LinkedList are:
- Java LinkedList class can contain duplicate elements.
- Java LinkedList class maintains insertion order.
- Java LinkedList class is non synchronized.
- In Java LinkedList class, manipulation is fast because no shifting needs to be occurred.
- Java LinkedList class can be used as list, stack or queue.
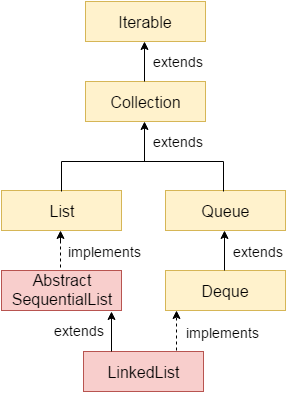
Hierarchy of LinkedList class
As shown in above diagram, Java LinkedList class extends AbstractSequentialList class and implements List and Deque interfaces.
Doubly Linked List
In case of doubly linked list, we can add or remove elements from both side.

LinkedList class declaration
Let's see the declaration for java.util.LinkedList class.
Constructors of Java LinkedList
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| LinkedList() | It is used to construct an empty list. |
| LinkedList(Collection c) | It is used to construct a list containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's iterator. |
Methods of Java LinkedList
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void add(int index, Object element) | It is used to insert the specified element at the specified position index in a list. |
| void addFirst(Object o) | It is used to insert the given element at the beginning of a list. |
| void addLast(Object o) | It is used to append the given element to the end of a list. |
| int size() | It is used to return the number of elements in a list |
| boolean add(Object o) | It is used to append the specified element to the end of a list. |
| boolean contains(Object o) | It is used to return true if the list contains a specified element. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | It is used to remove the first occurence of the specified element in a list. |
| Object getFirst() | It is used to return the first element in a list. |
| Object getLast() | It is used to return the last element in a list. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in a list of the first occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in a list of the last occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
Java LinkedList Example
Output:Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
Java HashSet class

Java HashSet class is used to create a collection that uses a hash table for storage. It inherits the AbstractSet class and implements Set interface.
The important points about Java HashSet class are:
- HashSet stores the elements by using a mechanism called hashing.
- HashSet contains unique elements only.
Difference between List and Set
List can contain duplicate elements whereas Set contains unique elements only.
Hierarchy of HashSet class
The HashSet class extends AbstractSet class which implements Set interface. The Set interface inherits Collection and Iterable interfaces in hierarchical order.
HashSet class declaration
Let's see the declaration for java.util.HashSet class.
Constructors of Java HashSet class:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| HashSet() | It is used to construct a default HashSet. |
| HashSet(Collection c) | It is used to initialize the hash set by using the elements of the collection c. |
| HashSet(int capacity) | It is used to initialize the capacity of the hash set to the given integer value capacity. The capacity grows automatically as elements are added to the HashSet. |
Methods of Java HashSet class:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void clear() | It is used to remove all of the elements from this set. |
| boolean contains(Object o) | It is used to return true if this set contains the specified element. |
| boolean add(Object o) | It is used to adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. |
| boolean isEmpty() | It is used to return true if this set contains no elements. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | It is used to remove the specified element from this set if it is present. |
| Object clone() | It is used to return a shallow copy of this HashSet instance: the elements themselves are not cloned. |
| Iterator iterator() | It is used to return an iterator over the elements in this set. |
| int size() | It is used to return the number of elements in this set. |
Java HashSet Example
OUTPUT:
Ajay
Vijay
Ravi
Java LinkedHashSet class

Java LinkedHashSet class is a Hash table and Linked list implementation of the set interface. It inherits HashSet class and implements Set interface.
The important points about Java LinkedHashSet class are:
- Contains unique elements only like HashSet.
- Provides all optional set operations, and permits null elements.
- Maintains insertion order.
Hierarchy of LinkedHashSet class
The LinkedHashSet class extends HashSet class which implements Set interface. The Set interface inherits Collection and Iterable interfaces in hierarchical order.
Example of LinkedHashSet class:
OUTPUT:
Ravi
Vijay
Ajay
Java TreeSet class

Java TreeSet class implements the Set interface that uses a tree for storage. It inherits AbstractSet class and implements NavigableSet interface. The objects of TreeSet class are stored in ascending order.
The important points about Java TreeSet class are:
- Contains unique elements only like HashSet.
- Access and retrieval times are quiet fast.
- Maintains ascending order.
Hierarchy of TreeSet class
As shown in above diagram, Java TreeSet class implements NavigableSet interface. The NavigableSet interface extends SortedSet, Set, Collection and Iterable interfaces in hierarchical order.
Java TreeSet Example
Output:
Ajay
Ravi
Vijay
Java Queue Interface
Java Queue interface orders the element in FIFO(First In First Out) manner. In FIFO, first element is removed first and last element is removed at last.
PriorityQueue class
The PriorityQueue class provides the facility of using queue. But it does not orders the elements in FIFO manner. It inherits AbstractQueue class.
Comments
Post a Comment