Industrial training in CDAC
6 Months industrial training
Android App Development
DAY 1
JAVA
Language:the method of human communication, either spoken or written, consisting of the use of words in a structured and conventional way.
Programming Language: A programming language is a formal language that specifies a set of instructions that can be used to produce various kinds of output. Programming languages generally consist of instructions for a computer.
JAVA: Java is a general-purpose computer-programming language that is concurrent, class-based, object-oriented, and specifically designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible.JAVA is a pure object oriented programming language.
FEATURES OF OOPS
The Objects Oriented programming language supports all the features of normal programming languages. In addition it supports some important concepts and terminology which has made it popular among programming methodology.
The important features of Object Oriented programming are:
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Data Hiding
- Encapsulation
- Overloading
- Reusability
Let us see a brief overview of these important features of Object Oriented programming
But before that it is important to know some new terminologies used in Object Oriented programming namely
- Objects
- Classes
Objects:
In other words object is an instance of a class.
Classes:
These contain data and functions bundled together under a unit. In other words class is a collection of similar objects. When we define a class it just creates template or Sekelton. So no memory is created when class is created. Memory is occupied only by object. In other words classes acts as data types for objects.
Member functions:
The functions defined inside the class as above are called member functions.
Here the concept of Data Hiding figures
Data Hiding:
This concept is the main heart of an Object oriented programming. The data is hidden inside the class by declaring it as private inside the class. When data or functions are defined as private it can be accessed only by the class in which it is defined. When data or functions are defined as public then it can be accessed anywhere outside the class. Object Oriented programming gives importance to protecting data which in any system. This is done by declaring data as private and making it accessible only to the class in which it is defined. This concept is called data hiding. But one can keep member functions as public. The technical term for combining data and functions together as a bundle is encapsulation.
Inheritance:
Inheritance as the name suggests is the concept of inheriting or deriving properties of an exiting class to get new class or classes. In other words we may have common features or characteristics that may be needed by number of classes. So those features can be placed in a common tree class called base class and the other classes which have these characteristics can take the tree class and define only the new things that they have on their own in their classes. These classes are called derived class. The main advantage of using this concept of inheritance in Object oriented programming is it helps in reducing the code size since the common characteristic is placed separately called as base class and it is just referred in the derived class. This provide the users the important usage of terminology called as reusability
Reusability:
This usage is achieved by the above explained terminology called as inheritance. Reusability is nothing but re- usage of structure without changing the existing one but adding new features or characteristics to it. It is very much needed for any programmers in different situations. Reuseability gives the following advantages to users. It helps in reducing the code size since classes can be just derived from existing one and one need to add only the new features and it helps users to save their time.
For instance if there is a class defined to draw different graphical figures say there is a user who want to draw graphical figure and also add the features of adding color to the graphical figure. In this scenario instead of defining a class to draw a graphical figure and coloring it what the user can do is make use of the existing class for drawing graphical figure by deriving the class and add new feature to the derived class namely add the feature of adding colors to the graphical figure.
Polymorphism and Overloading:
Poly refers many. So Polymorphism as the name suggests is a certain item appearing in different forms or ways. That is making a function or operator to act in different forms depending on the place they are present is called Polymorphism. Overloading is a kind of polymorphism. In other words say for instance we know that +, – operate on integer data type and is used to perform arithmetic additions and subtractions. But operator overloading is one in which we define new operations to these operators and make them operate on different data types in other words overloading the existing functionality with new one. This is a very important feature of object oriented programming methodology which extended the handling of data type and operations.
Thus the above given important features of object oriented programming among the numerous features it have gives the following advantages to the programming world. The advantages are namely
• Data Protection or security of data is achieved by concept of data hiding
• Reduces program size and saves time by the concept of reusability which is achieved by the terminology of Inheritance
• Operators can be given new functions as per user which extends the usage.
HISTORY OF JAVA
1) James Gosling, Mike Sheridan, and Patrick Naughton initiated the Java language project in June 1991. The small team of sun engineers called Green Team.
2) Originally designed for small, embedded systems in electronic appliances like set-top boxes.
3) Firstly, it was called "Greentalk" by James Gosling and file extension was .gt.
4) After that, it was called Oak and was developed as a part of the Green project.
Why Java named as "Oak"
5) Why Oak? Oak is a symbol of strength and choosen as a national tree of many countries like U.S.A., France, Germany, Romania etc.
6) In 1995, Oak was renamed as "Java" because it was already a trademark by Oak Technologies.
FEATURES OF JAVA
The Java language features are more fully described below:
Simple. Java was designed with a small number of language constructs so that programmers could learn it quickly. It eliminates several language features available in C/C++ that are associated with poor programming practices or rarely used: goto statements, header files, structures, operator overloading, multiple inheritance and pointers.
Object-oriented. Java is an OOPL that supports the construction of programs that consist of collections of collaborating objects. These objects have a unique identity, encapsulate attributes and operations, and are instances of classes related by inheritance and polymorphism.
Distributed. Java is designed to support various levels of network connectivity. Java applications are network aware: TCP/IP support is built into Java class libraries. They can open and access remote objects on the Internet.
Interpreted. Java is compiled to bytecodes, which are interpreted by a Java run-time environment.
Robust. Java is designed to eliminate certain types of programming errors. Java is strongly typed, which allows extensive compile-time error checking. It does not support memory pointers, which eliminates the possibility of overwriting memory and corrupting data. In addition, its automatic memory management (garbage collection) eliminates memory leaks and other problems associated with dynamic memory allocation/de-allocation.
Secure. Java is designed to be secure in a networked environment. The Java run-time environment uses a bytecode verification process to ensure that code loaded over the network does not violate Java security constraints.
Architecture neutral. Java applications that are compiled to bytecodes can be interpreted by any system that implements the Java Virtual Machine. Since the Java Virtual Machine is supported across most operating systems, this means that Java applications are able to run on most platforms.
Portable. In addition to supporting architecture neutrality, Java ensures that other implementation-dependent aspects of language specification are eliminated. For example, Java specifies the sizes of primitive data types and their arithmetic behavior.
High performance. Although Java is an interpreted language, it was designed to support “just-in-time” compilers, which dynamically compile bytecodes to machine code.
Multithreaded. Java supports multiple threads of execution (a.k.a., lightweight processes), including a set of synchronization primitives. This makes programming with threads much easier.
Dynamic language. Java supports dynamic loading of classes (a.k.a. “load on demand”), dynamic compilation, and automatic memory management (garbage collection).
IDENTIFIERS:In programming languages, identifiers are used for identification purpose. In Java an identifier can be a class name, method name, variable name or a label.
Rules for defining Java Identifiers
There are certain rules for defining a valid java identifiers. These rules must be followed, otherwise we get compile-time error. These rules are also valid for other languages like C,C++.
- The only allowed characters for identifiers are all alphanumeric characters([A-Z],[a-z],[0-9]), ‘$‘(dollar sign) and ‘_‘ (underscore).For example “geek@” is not a valid java identifier as it contain ‘@’ – special character.
- Identifiers should not start with digits([0-9]). For example “123geeks” is a not a valid java identifier.
- Java identifiers are case-sensitive.
- There is no limit on the length of the identifier but it is advisable to use an optimum length of 4 – 15 letters only.
- Reserved Words can’t be used as an identifier. For example “int while = 20;” is an invalid statement as while is a reserved word. There are 53 reserved words in Java.
LITERALS: Any constant value which can be assigned to the variable is called as literal/constant.
KEYWORDS: In the Java programming language, a keyword is one of 50 reserved words that have a predefined meaning in the language; because of this, programmers cannot use keywords as names for variables, methods, classes, or as any other identifier.
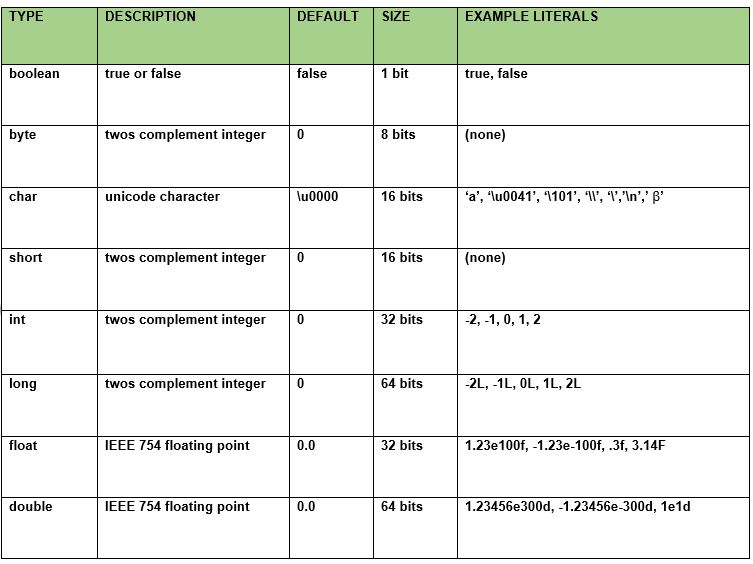
DATA TYPES: Java has two categories of data:
- Primitive data (e.g., number, character)
- Object data (programmer created types)
TYPE CASTING:
Type Casting in Java is nothing but converting a primitive or interface or class in Java into other type. There is a rule in Java Language that classes or interface which shares the same type hierarachy only can be typecasted. If there is no relationship between then Java will throw ClassCastException. Type casting are of two types they are
- Implicit Casting (Widening).
- Explicit Casting (Narrowing).
Widening conversions (Implicit casting)
A value of narrower(lower size) data type can be converted to a value of a broader (higher size) data type without loss of information is called Widening conversion. This conversion also known as implicit casting .
int i =1000;
double j=i;
In above example, an Automatic Type Casting take place, that is an integer variable (4 Byte) converted into double variable(8 Byte). The casting happened from a lower data type to a higher data type, so there is no data loss .
Narrowing Conversions (Explicit Casting)
Converting from a broader data type (higher size) to a narrower data type (lower size) is called narrowing conversion. This type of conversion can result in loss of information. This is not done implicitly by the JVM and requires explicit casting .
double i=100.7;
int j =(int) i;
In above example a double variable(8 Byte) converted into integer variable (4 Byte) . The casting happened from a higher data type to a lower data type, so can result in loss of information.
SCOPE AND VISIBILITY OF VARIABLES:
The scope of a variable defines the section of the code in which the variable is visible. As a general rule, variables that are defined within a block are not accessible outside that block. The lifetime of a variable refers to how long the variable exists before it is destroyed. Destroying variables refers to deallocating the memory that was allotted to the variables when declaring it. We have written a few classes till now. You might have observed that not all variables are the same. The ones declared in the body of a method were different from those that were declared in the class itself. There are there types of variables: instance variables, formal parameters or local variables and local variables.
ARRAYS:
An array is a group of like-typed variables that are referred to by a common name.Arrays in Java work differently than they do in C/C++. Following are some important point about Java arrays.
- In Java all arrays are dynamically allocated.(discussed below)
- Since arrays are objects in Java, we can find their length using member length. This is different from C/C++ where we find length using sizeof.
- A Java array variable can also be declared like other variables with [] after the data type.
- The variables in the array are ordered and each have an index beginning from 0.
- Java array can be also be used as a static field, a local variable or a method parameter.
- The size of an array must be specified by an int value and not long or short.
- The direct superclass of an array type is Object.
- Every array type implements the interfaces Cloneable and java.io.Serializable.
Array can contains primitives data types as well as objects of a class depending on the definition of array. In case of primitives data types, the actual values are stored in contiguous memory locations. In case of objects of a class, the actual objects are stored in heap segment.
TYPES OF ARRAY:
One-Dimensional Arrays :
The general form of a one-dimensional array declaration is
The general form of a one-dimensional array declaration is
type var_name;
or
type[] var_name;
An array declaration has two components: the type and the name. type declares the element type of the array. The element type determines the data type of each element that comprises the array. Like array of int type, we can also create an array of other primitive data types like char, float, double..etc or user defined data type(objects of a class).Thus, the element type for the array determines what type of data the array will hold.
Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays with each element of the array holding the reference of other array. These are also known as Jagged Array. A multidimensional array is created by appending one set of square brackets ([]) per dimension. Examples:
class multiDimensional{ public static void main(String args[]) { // declaring and initializing 2D array int arr[][] = { {2,7,9},{3,6,1},{7,4,2} }; // printing 2D array for (int i=0; i< 3 ; i++) { for (int j=0; j < 3 ; j++) System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " "); System.out.println(); } }}
Comments
Post a Comment